Google Chrome has several hidden features and experiments that can be enabled using special flags. These flags allow you to test upcoming features or tweak Chrome’s behavior. Enabling or disabling flags can help improve Chrome’s performance, accessibility, security, and more. Here’s a guide on how to enable and disable Google Chrome flags:
Key Takeaways
- Chrome flags are hidden experimental features that let you test upcoming additions to the browser.
- To enable a flag, go to chrome://flags, set it to “Enabled,” and restart Chrome. Disable flags by setting them back to “Default.”
- Valid flags include tab hover previews, scrollable tab strips, dark mode, and reader mode. Avoid too many flags at once.
- Flags can introduce bugs or instability, so don’t rely on them for mission-critical browsing. Disable any problematic flags.
- You can back up enabled flags or sync settings across devices. Resetting flags gets Chrome back to a stable default state.
What are Google Chrome Flags?
Chrome flags are experimental features under development but not yet ready for prime time. They allow developers and early adopters to test-drive new functionality. Flags can enable useful new tools or optimizations but may also have bugs or stability issues since they haven’t completed testing.
Flags are “hidden” because they are unavailable in Chrome by default. You have to enable them to turn on their functionality specifically. Once enabled, flags will remain active until you disable them or do a clean reinstallation of Chrome.
How to Open Chrome Flags?
To open the flags page:
Step 1.
Open Google Chrome.

Step 2.
Type chrome://flags into the Omnibox and hit Enter. This will open the “Experiments” page.
The flags page lists available experimental features you can enable or disable.
How to Enable a Flag?
To enable an experimental flag:
Step 1.
Find the flag you want to test. You can explore or scroll through the list.
Step 2.
Next to the flag, click the dropdown box and select “Enabled.”
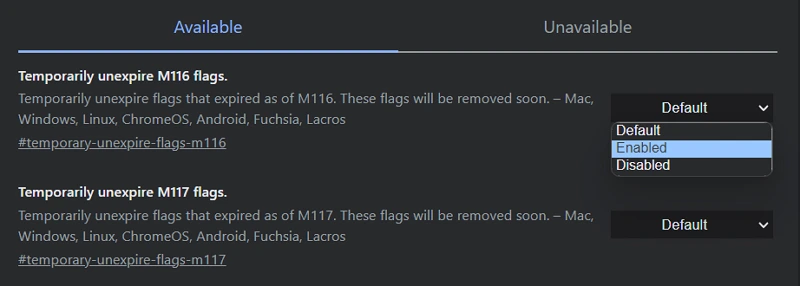
Restart Google Chrome by closing all tabs and windows. This will activate the flag. Test the experimental feature. Provide feedback if possible.
For example, to enable tab hovering, find the “Tab Hover Cards” flag, set it to Enabled, and restart Chrome. Now, you can hover over a tab to preview the page.
How to Disable Flags?
To turn off a flag:
Step 1.
Go back to chrome://flags.
Step 2.
Change the dropdown box from “Enabled” to “Default” or “Disabled.”
Restart the Chrome browser. The flag should be deactivated. Make sure to disable non-functioning or problematic flags. Leaving them on may cause issues.
Resettings Google Chrome Flags
To reset flags to their default settings:
Step 1.
Click the “Reset all to default” link at the bottom of the flags page.

Step 2.
Confirm you want to reset the flags. Relaunch Chrome.
Resetting removes any customizations and restores flags to their default state.
Useful Flags to Enable
There are some cool and valuable flags you can try out in Chrome. One is Tab Hover Cards, which allows you to preview tabs by hovering over them. Another is the Scrollable tab strip, which lets you scroll through open tabs horizontally.

Chrome also has flags for Touch Screen overlays that improve touch controls, Dark mode that enables a black UI theme, Reader mode that simplifies web pages for distraction-free reading, and Quieter audio muting that mutes tabs even when not the active tab.
Flags can let you customize and optimize your Chrome browsing experience, but use them judiciously.
When to Avoid Using Flags
Sometimes, it is best to avoid enabling experimental flags in Chrome. If you need stability more than early access to new features, it is wise not to risk bugs from unfinished flags and instead stick to the stable Chrome build.
On shared or work devices, experimental features enabled through flags may get turned on accidentally, so keeping flags at default prevents confusion. If you are uncomfortable tinkering with browser settings, unused flags are best left disabled, as changing defaults unnecessarily increases the chance of issues arising.
Chrome OS devices used in schools or businesses should generally not activate flags, as admins need consistency across the machines relying on Chrome. Before big presentations, interviews, travel, or other significant events, when you want reliability, it is best to use a normal Chrome build without flags enabled – experimental features can wait for less critical times.
If you prioritize having a smooth, predictable browsing experience, minimizing flags is a wise approach. However, they do provide early access for those comfortable testing new features.
Backing Up Google Chrome Flags
If you have enabled several flags to customize Chrome’s behavior, it can be hard to remember your settings if you need to reset or reinstall the browser.
Back up your list of enabled flags to avoid losing your flag setup. One way is to manually copy or screenshot the chrome://flags page to note the active flags. You can also right-click on the flags page and save it as an HTML file to store and refer back to later.
Some extensions, like ChFlags, can export your enabled flags as a file for safekeeping. Another option is to sync Chrome settings via your Google account, which retains flag statuses across devices and reinstalls.
With a backup of your flags on hand through one of these methods, you can easily replicate your flag setup if needed after resetting Chrome. Taking a few minutes to back up your enabled experimental flags will give you peace of mind that you can restore your custom Chrome configuration.
Crazy Facts
- A flag called “Force Dark Mode” will force dark mode on every website, even ones that don’t support it natively. It’s excellent for night browsing but can make some sites hard to read.
- Enabling the “Tab Grid Layout” flag makes Chrome display open tabs in a grid layout instead of a single row. It’s handy for tab hoarders but easy to get lost.
- The “Read Later” flag adds a new right-click option to save tabs for reading offline later. It’s great for catching up on articles, but it’s buggy.
- Turning on “Maximum Zoom” removes the default zoom limit so sites can be zoomed 5000% or more. Extremely impractical but fun for wasting time.
- There’s an option to make Chrome super lightweight via the “Chromium Diet” flag. It disables non-essential features and resources – speedy but barebones.
Conclusion
Chrome flags allow you to trial-run new features before they get officially launched. Enable them with care and reboot Chrome to start testing. Make sure to disable flags that cause problems or are no longer needed.
Resetting flags gets Chrome back to a clean, stable state. With some prudent experimentation, flags can give you early access to tools that boost your browsing experience.
FAQs about Enable and Disable Google Chrome Flags
Do flags drain the battery or slow down Chrome?
In most cases, no. Flags are designed to have minimal impact on Chrome’s performance. However, some experimental features may use more resources. Monitor any change after enabling a flag. Disable it if Chrome seems sluggish.
Will flags alter my browser data or settings?
Flags are isolated from your browsing data and should not affect saved settings, bookmarks, history, etc. However, some flags may change Chrome’s appearance or defaults.
I hope you enjoy our article. Do check out more of our amazing articles.
